torch.nn.quantized¶
This module implements the quantized versions of the nn modules and functionals.
Functional interface¶
Functional interface (quantized).
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.linear(input, weight, bias=None, scale=None, zero_point=None)[source]¶ Applies a linear transformation to the incoming quantized data: . See
LinearNote
Current implementation packs weights on every call, which has penalty on performance. If you want to avoid the overhead, use
Linear.- Parameters
input (Tensor) – Quantized input of type torch.quint8
weight (Tensor) – Quantized weight of type torch.qint8
bias (Tensor) – None or fp32 bias of type torch.float
scale (double) – output scale. If None, derived from the input scale
zero_point (long) – output zero point. If None, derived from the input zero_point
- Shape:
Input: where * means any number of additional dimensions
Weight:
Bias:
Output:
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.conv1d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.quint8)[source]¶ Applies a 1D convolution over a quantized 1D input composed of several input planes.
See
Conv1dfor details and output shape.- Parameters
input – quantized input tensor of shape
weight – quantized filters of shape
bias – non-quantized bias tensor of shape . The tensor type must be torch.float.
stride – the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple (sW,). Default: 1
padding – implicit paddings on both sides of the input. Can be a single number or a tuple (padW,). Default: 0
dilation – the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple (dW,). Default: 1
groups – split input into groups, should be divisible by the number of groups. Default: 1
padding_mode – the padding mode to use. Only “zeros” is supported for quantized convolution at the moment. Default: “zeros”
scale – quantization scale for the output. Default: 1.0
zero_point – quantization zero_point for the output. Default: 0
dtype – quantization data type to use. Default:
torch.quint8
Examples:
>>> from torch.nn.quantized import functional as qF >>> filters = torch.randn(33, 16, 3, dtype=torch.float) >>> inputs = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, dtype=torch.float) >>> bias = torch.randn(33, dtype=torch.float) >>> >>> scale, zero_point = 1.0, 0 >>> dtype_inputs = torch.quint8 >>> dtype_filters = torch.qint8 >>> >>> q_filters = torch.quantize_per_tensor(filters, scale, zero_point, dtype_filters) >>> q_inputs = torch.quantize_per_tensor(inputs, scale, zero_point, dtype_inputs) >>> qF.conv1d(q_inputs, q_filters, bias, padding=1, scale=scale, zero_point=zero_point)
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.quint8)[source]¶ Applies a 2D convolution over a quantized 2D input composed of several input planes.
See
Conv2dfor details and output shape.- Parameters
input – quantized input tensor of shape
weight – quantized filters of shape
bias – non-quantized bias tensor of shape . The tensor type must be torch.float.
stride – the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple (sH, sW). Default: 1
padding – implicit paddings on both sides of the input. Can be a single number or a tuple (padH, padW). Default: 0
dilation – the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple (dH, dW). Default: 1
groups – split input into groups, should be divisible by the number of groups. Default: 1
padding_mode – the padding mode to use. Only “zeros” is supported for quantized convolution at the moment. Default: “zeros”
scale – quantization scale for the output. Default: 1.0
zero_point – quantization zero_point for the output. Default: 0
dtype – quantization data type to use. Default:
torch.quint8
Examples:
>>> from torch.nn.quantized import functional as qF >>> filters = torch.randn(8, 4, 3, 3, dtype=torch.float) >>> inputs = torch.randn(1, 4, 5, 5, dtype=torch.float) >>> bias = torch.randn(8, dtype=torch.float) >>> >>> scale, zero_point = 1.0, 0 >>> dtype_inputs = torch.quint8 >>> dtype_filters = torch.qint8 >>> >>> q_filters = torch.quantize_per_tensor(filters, scale, zero_point, dtype_filters) >>> q_inputs = torch.quantize_per_tensor(inputs, scale, zero_point, dtype_inputs) >>> qF.conv2d(q_inputs, q_filters, bias, padding=1, scale=scale, zero_point=zero_point)
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.conv3d(input, weight, bias, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.quint8)[source]¶ Applies a 3D convolution over a quantized 3D input composed of several input planes.
See
Conv3dfor details and output shape.- Parameters
input – quantized input tensor of shape
weight – quantized filters of shape
bias – non-quantized bias tensor of shape . The tensor type must be torch.float.
stride – the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple (sD, sH, sW). Default: 1
padding – implicit paddings on both sides of the input. Can be a single number or a tuple (padD, padH, padW). Default: 0
dilation – the spacing between kernel elements. Can be a single number or a tuple (dD, dH, dW). Default: 1
groups – split input into groups, should be divisible by the number of groups. Default: 1
padding_mode – the padding mode to use. Only “zeros” is supported for quantized convolution at the moment. Default: “zeros”
scale – quantization scale for the output. Default: 1.0
zero_point – quantization zero_point for the output. Default: 0
dtype – quantization data type to use. Default:
torch.quint8
Examples:
>>> from torch.nn.quantized import functional as qF >>> filters = torch.randn(8, 4, 3, 3, 3, dtype=torch.float) >>> inputs = torch.randn(1, 4, 5, 5, 5, dtype=torch.float) >>> bias = torch.randn(8, dtype=torch.float) >>> >>> scale, zero_point = 1.0, 0 >>> dtype_inputs = torch.quint8 >>> dtype_filters = torch.qint8 >>> >>> q_filters = torch.quantize_per_tensor(filters, scale, zero_point, dtype_filters) >>> q_inputs = torch.quantize_per_tensor(inputs, scale, zero_point, dtype_inputs) >>> qF.conv3d(q_inputs, q_filters, bias, padding=1, scale=scale, zero_point=zero_point)
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False, return_indices=False)[source]¶ Applies a 2D max pooling over a quantized input signal composed of several quantized input planes.
Note
The input quantization parameters are propagated to the output.
See
MaxPool2dfor details.
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(input, output_size)[source]¶ Applies a 2D adaptive average pooling over a quantized input signal composed of several quantized input planes.
Note
The input quantization parameters propagate to the output.
See
AdaptiveAvgPool2dfor details and output shape.- Parameters
output_size – the target output size (single integer or double-integer tuple)
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.avg_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, ceil_mode=False, count_include_pad=True, divisor_override=None)[source]¶ Applies 2D average-pooling operation in regions by step size steps. The number of output features is equal to the number of input planes.
Note
The input quantization parameters propagate to the output.
See
AvgPool2dfor details and output shape.- Parameters
input – quantized input tensor
kernel_size – size of the pooling region. Can be a single number or a tuple (kH, kW)
stride – stride of the pooling operation. Can be a single number or a tuple (sH, sW). Default:
kernel_sizepadding – implicit zero paddings on both sides of the input. Can be a single number or a tuple (padH, padW). Default: 0
ceil_mode – when True, will use ceil instead of floor in the formula to compute the output shape. Default:
Falsecount_include_pad – when True, will include the zero-padding in the averaging calculation. Default:
Truedivisor_override – if specified, it will be used as divisor, otherwise size of the pooling region will be used. Default: None
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.interpolate(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None)[source]¶ Down/up samples the input to either the given
sizeor the givenscale_factorSee
torch.nn.functional.interpolate()for implementation details.The input dimensions are interpreted in the form: mini-batch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width.
Note
The input quantization parameters propagate to the output.
Note
Only 2D/3D input is supported for quantized inputs
Note
Only the following modes are supported for the quantized inputs:
bilinear
nearest
- Parameters
input (Tensor) – the input tensor
size (int or Tuple[int] or Tuple[int, int] or Tuple[int, int, int]) – output spatial size.
scale_factor (float or Tuple[float]) – multiplier for spatial size. Has to match input size if it is a tuple.
mode (str) – algorithm used for upsampling:
'nearest'|'bilinear'align_corners (bool, optional) – Geometrically, we consider the pixels of the input and output as squares rather than points. If set to
True, the input and output tensors are aligned by the center points of their corner pixels, preserving the values at the corner pixels. If set toFalse, the input and output tensors are aligned by the corner points of their corner pixels, and the interpolation uses edge value padding for out-of-boundary values, making this operation independent of input size whenscale_factoris kept the same. This only has an effect whenmodeis'bilinear'. Default:False
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.hardswish(input, scale, zero_point)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
hardswish().- Parameters
input – quantized input
scale – quantization scale of the output tensor
zero_point – quantization zero point of the output tensor
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.upsample(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None)[source]¶ Upsamples the input to either the given
sizeor the givenscale_factorWarning
This function is deprecated in favor of
torch.nn.quantized.functional.interpolate(). This is equivalent withnn.quantized.functional.interpolate(...).See
torch.nn.functional.interpolate()for implementation details.The input dimensions are interpreted in the form: mini-batch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width.
Note
The input quantization parameters propagate to the output.
Note
Only 2D input is supported for quantized inputs
Note
Only the following modes are supported for the quantized inputs:
bilinear
nearest
- Parameters
input (Tensor) – quantized input tensor
size (int or Tuple[int] or Tuple[int, int] or Tuple[int, int, int]) – output spatial size.
scale_factor (float or Tuple[float]) – multiplier for spatial size. Has to be an integer.
mode (string) – algorithm used for upsampling:
'nearest'|'bilinear'align_corners (bool, optional) – Geometrically, we consider the pixels of the input and output as squares rather than points. If set to
True, the input and output tensors are aligned by the center points of their corner pixels, preserving the values at the corner pixels. If set toFalse, the input and output tensors are aligned by the corner points of their corner pixels, and the interpolation uses edge value padding for out-of-boundary values, making this operation independent of input size whenscale_factoris kept the same. This only has an effect whenmodeis'bilinear'. Default:False
Warning
With
align_corners = True, the linearly interpolating modes (bilinear) don’t proportionally align the output and input pixels, and thus the output values can depend on the input size. This was the default behavior for these modes up to version 0.3.1. Since then, the default behavior isalign_corners = False. SeeUpsamplefor concrete examples on how this affects the outputs.
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.upsample_bilinear(input, size=None, scale_factor=None)[source]¶ Upsamples the input, using bilinear upsampling.
Warning
This function is deprecated in favor of
torch.nn.quantized.functional.interpolate(). This is equivalent withnn.quantized.functional.interpolate(..., mode='bilinear', align_corners=True).Note
The input quantization parameters propagate to the output.
Note
Only 2D inputs are supported
-
torch.nn.quantized.functional.upsample_nearest(input, size=None, scale_factor=None)[source]¶ Upsamples the input, using nearest neighbours’ pixel values.
Warning
This function is deprecated in favor of
torch.nn.quantized.functional.interpolate(). This is equivalent withnn.quantized.functional.interpolate(..., mode='nearest').Note
The input quantization parameters propagate to the output.
Note
Only 2D inputs are supported
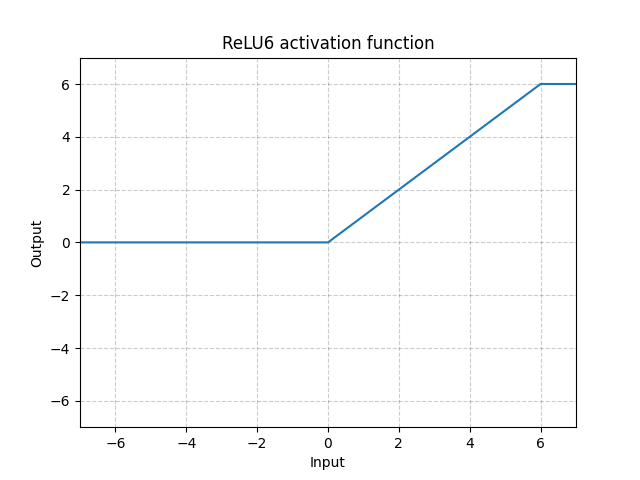
ReLU6¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.ReLU6(inplace=False)[source]¶ Applies the element-wise function:
, where is the zero_point, and is the quantized representation of number 6.
- Parameters
inplace – can optionally do the operation in-place. Default:
False
- Shape:
Input: where * means, any number of additional dimensions
Output: , same shape as the input
Examples:
>>> m = nn.quantized.ReLU6() >>> input = torch.randn(2) >>> input = torch.quantize_per_tensor(input, 1.0, 0, dtype=torch.qint32) >>> output = m(input)
ELU¶
Hardswish¶
Conv1d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')[source]¶ Applies a 1D convolution over a quantized input signal composed of several quantized input planes.
For details on input arguments, parameters, and implementation see
Conv1d.Note
Only zeros is supported for the
padding_modeargument.Note
Only torch.quint8 is supported for the input data type.
- Variables
See
Conv1dfor other attributes.Examples:
>>> m = nn.quantized.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2) >>> input = torch.randn(20, 16, 100) >>> # quantize input to quint8 >>> q_input = torch.quantize_per_tensor(input, scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.quint8) >>> output = m(q_input)
Conv2d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')[source]¶ Applies a 2D convolution over a quantized input signal composed of several quantized input planes.
For details on input arguments, parameters, and implementation see
Conv2d.Note
Only zeros is supported for the
padding_modeargument.Note
Only torch.quint8 is supported for the input data type.
- Variables
See
Conv2dfor other attributes.Examples:
>>> # With square kernels and equal stride >>> m = nn.quantized.Conv2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2) >>> # non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding >>> m = nn.quantized.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2)) >>> # non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding and dilation >>> m = nn.quantized.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2), dilation=(3, 1)) >>> input = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100) >>> # quantize input to quint8 >>> q_input = torch.quantize_per_tensor(input, scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.quint8) >>> output = m(q_input)
Conv3d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.Conv3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')[source]¶ Applies a 3D convolution over a quantized input signal composed of several quantized input planes.
For details on input arguments, parameters, and implementation see
Conv3d.Note
Only zeros is supported for the
padding_modeargument.Note
Only torch.quint8 is supported for the input data type.
- Variables
See
Conv3dfor other attributes.Examples:
>>> # With square kernels and equal stride >>> m = nn.quantized.Conv3d(16, 33, 3, stride=2) >>> # non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding >>> m = nn.quantized.Conv3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 5), stride=(1, 2, 2), padding=(1, 2, 2)) >>> # non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding and dilation >>> m = nn.quantized.Conv3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 5), stride=(1, 2, 2), padding=(1, 2, 2), dilation=(1, 2, 2)) >>> input = torch.randn(20, 16, 56, 56, 56) >>> # quantize input to quint8 >>> q_input = torch.quantize_per_tensor(input, scale=1.0, zero_point=0, dtype=torch.quint8) >>> output = m(q_input)
FloatFunctional¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.FloatFunctional[source]¶ State collector class for float operations.
The instance of this class can be used instead of the
torch.prefix for some operations. See example usage below.Note
This class does not provide a
forwardhook. Instead, you must use one of the underlying functions (e.g.add).Examples:
>>> f_add = FloatFunctional() >>> a = torch.tensor(3.0) >>> b = torch.tensor(4.0) >>> f_add.add(a, b) # Equivalent to ``torch.add(a, b)``
- Valid operation names:
add
cat
mul
add_relu
add_scalar
mul_scalar
QFunctional¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.QFunctional[source]¶ Wrapper class for quantized operations.
The instance of this class can be used instead of the
torch.ops.quantizedprefix. See example usage below.Note
This class does not provide a
forwardhook. Instead, you must use one of the underlying functions (e.g.add).Examples:
>>> q_add = QFunctional() >>> a = torch.quantize_per_tensor(torch.tensor(3.0), 1.0, 0, torch.qint32) >>> b = torch.quantize_per_tensor(torch.tensor(4.0), 1.0, 0, torch.qint32) >>> q_add.add(a, b) # Equivalent to ``torch.ops.quantized.add(a, b, 1.0, 0)``
- Valid operation names:
add
cat
mul
add_relu
add_scalar
mul_scalar
Quantize¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.Quantize(scale, zero_point, dtype)[source]¶ Quantizes an incoming tensor
- Parameters
scale – scale of the output Quantized Tensor
zero_point – zero_point of output Quantized Tensor
dtype – data type of output Quantized Tensor
- Variables
zero_point, dtype (`scale`,) –
- Examples::
>>> t = torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., -1.]]) >>> scale, zero_point, dtype = 1.0, 2, torch.qint8 >>> qm = Quantize(scale, zero_point, dtype) >>> qt = qm(t) >>> print(qt) tensor([[ 1., -1.], [ 1., -1.]], size=(2, 2), dtype=torch.qint8, scale=1.0, zero_point=2)
DeQuantize¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.DeQuantize[source]¶ Dequantizes an incoming tensor
- Examples::
>>> input = torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., -1.]]) >>> scale, zero_point, dtype = 1.0, 2, torch.qint8 >>> qm = Quantize(scale, zero_point, dtype) >>> quantized_input = qm(input) >>> dqm = DeQuantize() >>> dequantized = dqm(quantized_input) >>> print(dequantized) tensor([[ 1., -1.], [ 1., -1.]], dtype=torch.float32)
Linear¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias_=True, dtype=torch.qint8)[source]¶ A quantized linear module with quantized tensor as inputs and outputs. We adopt the same interface as torch.nn.Linear, please see https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Linear for documentation.
Similar to
Linear, attributes will be randomly initialized at module creation time and will be overwritten later- Variables
~Linear.weight (Tensor) – the non-learnable quantized weights of the module of shape .
~Linear.bias (Tensor) – the non-learnable bias of the module of shape . If
biasisTrue, the values are initialized to zero.~Linear.scale – scale parameter of output Quantized Tensor, type: double
~Linear.zero_point – zero_point parameter for output Quantized Tensor, type: long
Examples:
>>> m = nn.quantized.Linear(20, 30) >>> input = torch.randn(128, 20) >>> input = torch.quantize_per_tensor(input, 1.0, 0, torch.quint8) >>> output = m(input) >>> print(output.size()) torch.Size([128, 30])
BatchNorm2d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
BatchNorm2d.
BatchNorm3d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.BatchNorm3d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
BatchNorm3d.
LayerNorm¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.LayerNorm(normalized_shape, weight, bias, scale, zero_point, eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
LayerNorm.- Additional args:
scale - quantization scale of the output, type: double.
zero_point - quantization zero point of the output, type: long.
GroupNorm¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.GroupNorm(num_groups, num_channels, weight, bias, scale, zero_point, eps=1e-05, affine=True)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
GroupNorm.- Additional args:
scale - quantization scale of the output, type: double.
zero_point - quantization zero point of the output, type: long.
InstanceNorm1d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.InstanceNorm1d(num_features, weight, bias, scale, zero_point, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=False, track_running_stats=False)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
InstanceNorm1d.- Additional args:
scale - quantization scale of the output, type: double.
zero_point - quantization zero point of the output, type: long.
InstanceNorm2d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.InstanceNorm2d(num_features, weight, bias, scale, zero_point, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=False, track_running_stats=False)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
InstanceNorm2d.- Additional args:
scale - quantization scale of the output, type: double.
zero_point - quantization zero point of the output, type: long.
InstanceNorm3d¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.InstanceNorm3d(num_features, weight, bias, scale, zero_point, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=False, track_running_stats=False)[source]¶ This is the quantized version of
InstanceNorm3d.- Additional args:
scale - quantization scale of the output, type: double.
zero_point - quantization zero point of the output, type: long.
Embedding¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.Embedding(num_embeddings, embedding_dim, padding_idx=None, max_norm=None, norm_type=2.0, scale_grad_by_freq=False, sparse=False, _weight=None, dtype=torch.quint8)[source]¶ A quantized Embedding module with quantized packed weights as inputs. We adopt the same interface as torch.nn.Embedding, please see https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Embedding for documentation.
Similar to
Embedding, attributes will be randomly initialized at module creation time and will be overwritten later- Variables
~Embedding.weight (Tensor) – the non-learnable quantized weights of the module of shape .
- Examples::
>>> m = nn.quantized.Embedding(num_embeddings=10, embedding_dim=12) >>> indices = torch.tensor([9, 6, 5, 7, 8, 8, 9, 2, 8]) >>> output = m(indices) >>> print(output.size()) torch.Size([9, 12]
EmbeddingBag¶
-
class
torch.nn.quantized.EmbeddingBag(num_embeddings, embedding_dim, max_norm=None, norm_type=2.0, scale_grad_by_freq=False, mode='sum', sparse=False, _weight=None, include_last_offset=False, dtype=torch.quint8)[source]¶ A quantized EmbeddingBag module with quantized packed weights as inputs. We adopt the same interface as torch.nn.EmbeddingBag, please see https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.EmbeddingBag for documentation.
Similar to
EmbeddingBag, attributes will be randomly initialized at module creation time and will be overwritten later- Variables
~EmbeddingBag.weight (Tensor) – the non-learnable quantized weights of the module of shape .
- Examples::
>>> m = nn.quantized.EmbeddingBag(num_embeddings=10, embedding_dim=12, include_last_offset=True, mode='sum') >>> indices = torch.tensor([9, 6, 5, 7, 8, 8, 9, 2, 8, 6, 6, 9, 1, 6, 8, 8, 3, 2, 3, 6, 3, 6, 5, 7, 0, 8, 4, 6, 5, 8, 2, 3]) >>> offsets = torch.tensor([0, 19, 20, 28, 28, 32]) >>> output = m(indices, offsets) >>> print(output.size()) torch.Size([5, 12]
